Fractures of Face
Fractures of
the Facial Skeleton
Confirmation of the exact site of fracture of bones of face is done by doing 3D CT Scan of face along with CT Scan of head done to rule out any head injury.
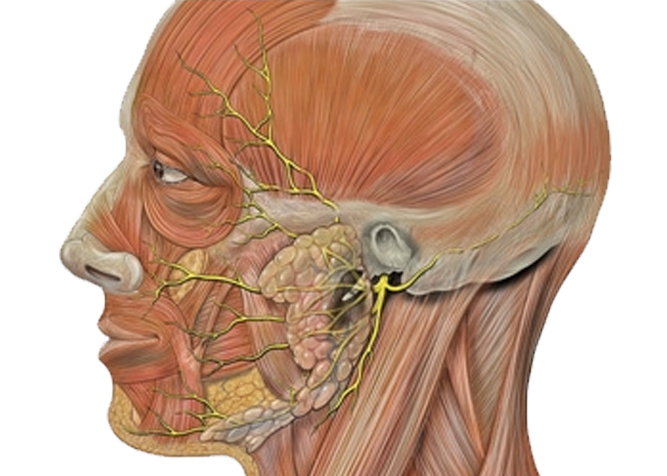
Best Fractures of Face Surgery in India
Fractures of the different bones of the face cause impaired function & give a distorted appearance to the face. The ability of a person to eat, speak & swallow is majorly affected.
Treatment of fractures of the face in case of trauma is very much dependent on the site, the number of bones involved and accompanying soft tissue injury, and also the age of the patient.
There could be accompanying Soft Tissue Injuries of the face which require management as per the location and size of the defect.
In children, fracture fixation must allow for continued growth & development of facial features & skull.
What are the different bones fractured on the face?
- Lower jaw (mandible)
- Upper jaw (maxilla)-LeFort fracture
- Cheekbone (zygoma)
- Nose
- Orbit
- Forehead (frontal)
PAN FACIAL Fracture - When multiple or all bones are fractured on the face.
NOE (Naso-Orbito-ethmoid) Fracture - Fracture of the Naso-orbito-ethmoid bone complex of the face.
What are the causes of Fractures of the face?
- Road accidents.
- Wounds.
- Sports Injury.
- Violence.
What are the things to remember in patients with fractures of the face?
- Airway damage - A broken nose or other fractures and swelling can injure the nasal passage and make it difficult for a person to breathe.
- Neurological problems - Facial injuries can be associated with head trauma that can have an impact on the skull and brain. Uneven pupils and a leak of clear cerebrospinal fluid from the nose are some signs that indicate the involvement of the brain.
- Fractures of the face can be associated with Internal bleeding - Bleed can cause increased pressure in the skull, putting the eyes, brain, nerves, or other sensitive structures at risk for further injury.
- There can be associated injuries to the chest, and organs of the abdomen.
- The diagnosis of fractures can be made by physical examination and confirmation is done by a 3D CT scan of the face
- Treatment of Facial Fractures is by one of the following procedures-
- Closed Reduction- Broken bones are reset manually without invasive surgery.
- Open Reduction- Surgically aligning the broken bones and fixing them with the help of wires or plates to stabilize the jaws and allow the bone to heal. This can call for a liquid diet regime for a few weeks.
- Dental treatment may be required for splinting or restorative procedures. Speech therapy for injuries in the tongue or mouth. The patient may also require psychological help to deal with the traumatic stress./li>
What is the initial management of patients with Fractures of the face?
Treatment involves basic trauma management and then treatment of specific fractures of the face.
- Making sure that the patient can breathe, if there is difficult breathing, it will be the first step in management
- Material may be present in the mouth that may block the airway should be removed
- Oxygen, if required
- Tracheal or nasal intubation (inserting a tube into the airway to assist breathing)
- Dressing of wounds
- Antibiotics
- Tetanus immunization
- Suturing of the Open wounds to stop bleeding
- Nasal packing to control nosebleed.
- Ice fomentation and pain killers
Confirmation of the exact site of fracture of bones of face is done by doing a 3D CT scan of face along with a 3DCT Scan of the head to rule out any head injury
Fracture Mandible (Lower Jaw)
Fracture mandible is a fracture in the lower jawbone. Few particular sites in the lower jawbone are more prone to fracture. After a fracture, the patient is unable to fully open the mouth, or the mouth opening is painful. Often alignment of teeth is disturbed and there may be tooth loss also.
These fractures are most common in young males and the main reason is road accidents and trauma during fights. OPG and Plain X-rays are used for diagnosis, but 3D CT scans are more commonly done these days to find the exact location of the fracture, and the amount of displacement of a broken bone and to rule out associated multiple fractures.
Surgical management is the key to the treatment of fractures of the lower jaw. The reduction of fractured bone fragments is the first step in managing the fracture of the lower jaw. It means approximating the broken bone edges as close together as possible.
- This can be done by manipulating the broken lower jaw which is called "closed reduction" and immobilizing the jaws (intermaxillary fixation-IMF) with an arch bar and stainless-steel wires for 4-6 weeks.
- "Open Reduction and Internal Fixation" technique or ORIF- An "open reduction" is the usually preferred technique in today's time as accurate reduction is possible with this method, where an incision is made, the fracture is found and is physically manipulated into place. This definitive reduction treatment is most of the time stabilized surgically by plates and screws fixation of the broken bones under vision so that fractured ends meet accurately.
- Apart from a fixation with plates and screws after the open reduction, the lower jaw can be immobilized with stainless steel wire woven across the fractured bone segments to avoid re-displacement of bony edges. If this method of reduction is used, the immobility of bone is maintained by the arch bar and stainless-steel wire Inter maxillary fixation for a minimum of 4 weeks.
There is no need for IMF to immobilize the jaws after the surgery with this technique. Various types of plates and screws are used depending on the type of fracture and patient factors.
The patient is usually discharged from the hospital on the second day after the surgery and is kept on a soft diet for 2 to 3 weeks.
Usually, the broken bone gains 80% of its normal strength by 3 weeks and 90% by 4 weeks.
Fracture Upper Jaw (Maxilla)
The maxilla is the bone of the upper jaw that stays fixed, unlike the mobile lower jaw. It also contributes to the bony skeleton of the eyes, nose and cheeks. Fractures of this bone are known as mid-face fractures and are classified into three types as per Le Fort classification.
- Le Fort I : This is the fracture in the upper jaw above and along the upper lip, separating the teeth apart from the maxillary bone, including the lower portion of the nose.
- Le Fort II : It is a pyramid-shaped fracture that involves the teeth at the base and the nasal bridge at its highest point, along with the eye sockets and extending up to nasal bones.
- Le Fort III : This fracture occurs across the nasal bridge, through the eye sockets, and outward to the sides of the face. This is the most complicated kind of upper jaw fracture and is caused due to severe blow to the face.
In fractures of the upper jaw, the patient is unable to fully open the mouth, or the mouth opening is painful. Often alignment of teeth is disturbed and there may be tooth loss also. The face appears elongated or concave or dish shaped.
A 3D CT scan of the face usually confirms the diagnosis, helps in the classification of the fracture patterns and aids in planning the surgery.
- Non-surgical approach for treatment is considered for minimal, non-displaced fractures, or in medically ill patients. This would include regular analgesia, a soft diet and taking care to avoid any trauma. Rest all the cases need surgical intervention.
- Surgery for Lefort fractures is necessary to maintain facial features and contour. And, like lower jaw, upper jaw fractures also need reduction and immobilization to heal. It means approximating the broken bone edges as close together as possible. Reduction manipulation of the broken jaw is done by closed approach or open surgical approach.
- This can be done by manipulating the broken upper jaw which is called "closed reduction" and immobilizing the jaws (intermaxillary fixation-IMF) with an arch bar and wires for 4-6 weeks.
- "Open Reduction and Internal Fixation" technique or ORIF- An "open reduction" is the usually preferred technique as accurate reduction is possible with this method, where an incision is made, the fracture is found and is physically manipulated into place. This definitive reduction treatment is most of the time stabilized surgically by plates and screws fixation of the broken bones under vision so that fractured ends meet accurately.
- Apart from a fixation with plates and screws after the open reduction, the upper jaw can be immobilized with stainless steel wire woven across the fractured bone segments to avoid re-displacement of bony edges. If this method of reduction is used, the immobility of bone is maintained by the arch bar and stainless-steel wire Inter maxillary fixation for a minimum of 4 weeks.
There is no need to immobilize the jaws in IMF after the surgery with this technique. Various types of plates and screws are used depending on the type of fracture and patient factors.
The patient is usually discharged from the hospital on the third day after the surgery and is kept on a soft diet for 2 to 3 weeks.
Usually, the broken bone gains 80% of its normal strength by 3 weeks and 90% by 4 weeks.
Fracture Cheek bone (Zygoma)
Zygoma is also known as the malar/cheekbone. Fractures of the Zygoma bone lead to cosmetic deformities mostly. Patients with cheekbone fractures can also have difficulty opening their mouths. These fractures are usually accompanied by fractures in the upper jaw (maxilla) and eye socket bone. A 3D CT scan of the face usually confirms the diagnosis.
- Non-surgical approach for the treatment of cheekbone fracture is considered for minimal, non-displaced fractures, or in medically ill patients. This would include regular analgesia, a soft diet and taking care to avoid any trauma. Rest all the cases need surgical intervention.
- Management of zygoma fractures is necessary to maintain facial features and contour. Reduction manipulation of the zygoma bone is done by an open surgical approach only. Incisions are made in such areas that scars are not visible to the human eye (within the hairline, inside the mouth or below the eyelashes). Fractures are found and physically manipulated into the correct place. The definitive treatment is most of the time done surgically by plates and screws fixation of the broken bones under vision so that fractured ends meet accurately. This is referred to as the "open reduction and internal fixation" technique or ORIF. Various types of plates and screws are used depending on the type of fracture and patient factors.
The patient is usually discharged from the hospital on the third day after the surgery and is kept on a soft diet for 2 to 3 weeks.
Fracture Nose
Fractures of the nose usually bleed profusely at the time of blow. So, the first step in management is to give external compression to control bleeding. It usually takes a few minutes to stop bleeding after which nasal packing is done.
Diagnosis is made clinically by feeling the crackling sound or the visible deviation of the nose bridge. X-ray usually confirms the diagnosis.
Treatment of the nasal bone fracture would depend on the time of presentation after the fracture.
- If the patient arrives early after the nose fracture, reduction of the bone and immobilization with a plaster slab over the nose is given.
- The reduction of the fracture is still possible conveniently till one week after the accident after which reduction becomes a little difficult as the fracture starts to unite in the wrong position after a week.
- This reduction becomes surgically difficult if three weeks have elapsed after the accident and bones would have united in the wrong position. So, in fractures of nasal bone which are more than 3 weeks old and the deformity is severe, refracture of nasal bones and correction of alignment is done.
Fracture forehead (Frontal bone)
The frontal bone is the main bone in the forehead area. A high-impact injury to the head can cause a fracture of the frontal bone and floor of the sinuses. The fracture is mostly likely to occur in the middle of the forehead. That's where the bone is the thinnest and weakest. An injury may cause the bone to be indented (pushed inward). Substantial force is required to fracture the frontal bone, so often other injuries to the face and skull or neurological trauma may be present. Associated problems may include leakage of the cerebrospinal fluid, eye injuries and damage to the sinus ducts. 3D CT scan of the face and head usually confirms the diagnosis. Treatment of frontal bone fracture-
- Simple undisplaced fractures are best left alone and no surgery is required.
- Displaced fractures with depressed forehead need surgery in form of open reduction and plate fixation.
Orbital fractures (eye socket)
Orbital fractures are the fractures of the bones of the eye socket around the eyeball. They are classified in two different ways:
- Orbital rim fracture- It includes fracture of the outer margin of the bony socket. The outer rim of the eyeball is a strong structure and is broken by a strong force or blow.
- Orbital floor fractures- In this case, the orbital rim is not damaged, instead, there is a break in the floor of the eye socket that leads to entanglement of eyeball structures into the fracture line or herniation of contents of the orbit into the maxillary sinus. It can cause symptoms like enophthalmos (sunken eye appearance), inability to move the eyeball upwards (due to muscle entrapment), double vision, severe pain and swelling etc.
A 3D CT scan of the face usually confirms the diagnosis of the orbit. Orbital fractures can be accompanied by fractures of the cheek bone, nose or upper jaw or can be a part of NOE complex fracture.
Treatment of eye socket fractures requires
- The conservative approach, if fracture is undisplaced or if not causing any symptoms.
- In cases of displaced orbital rim fracture or orbital floor fracture, urgent surgical intervention is needed.
- Orbital rim fractures are fixed by open reduction with lower blepharoplasty incision and fixation is done with low profile 1.5 mm plates and screws.
- Orbital floor fractures with double vision, sunken eye appearance and muscle entrapment, surgery is done. Surgical release of the soft structures of the eye is done with a lower blepharoplasty incision, close to the lower eyelashes so that the scar is imperceptible to the human eye after the surgery. After the release of the orbital septum and entrapped structures carefully, the orbital floor is supported with the metal mesh.
When orbital fractures are accompanied by nasal bone and ethmoid bone fractures, they are called NOE (Naso-orbito-ethmoid) fractures. NOE fractures lead to the depressed forehead-orbital-nose area and are very difficult and notorious to treat, and the best time is to treat them early than to be sorry for later.
When multiple bones of the face are fractured together, the condition is called PAN-FACIAL fracture. The management of PAN-facial fractures of the face is quite challenging and requires proper treatment policy, sequencing and plating algorithm for the various fractures of the face to maximise the functional and cosmetic outcome.
Know your surgeon better

Best plastic surgeon, Dr. Amit Agarwal is an American Board Certified, extensively trained, and best Plastic & Aesthetic surgeon in Lucknow. He is the Chief Plastic Surgeon heading the Department of Plastic, Microvascular, and Craniofacial surgery at Vivekananda Polyclinic and Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, U.P, India. He maintains a busy practice at Avadh and Nishat Hospital and his own center - Kayakriti Plastic Surgery & Dental Center. He was formerly a Consultant in the Department of Plastic Surgery and Burns at the prestigious SGPGI, Lucknow.
MS, DNB (General Surgery) MCh, DNB (Plastic Surgery),
MNAMS, FACS, FICS, FRCS (Edinburgh, UK)
His Credentials
Three pillars of kayakriti
Privacy
We believe your experience with us should be comfortable and hassle-free to make it one of your best lifetime experiences for yours. We, here at the clinic, take full precautions to maintain your privacy in any manner. We also provide a staff who will receive you from the gate and take you to the chamber directly if you demand.
Trust
Our Surgeon is highly qualified and internationally certified with a team of skilled staff to perform any surgical or non-surgical treatment on your body.
Safety
When you plan to undergo any surgery you should always keep in mind that it's your body and it's a surgery. We, here always keep your safety a priority and will never recommend you to undergo any such procedure which is not safe for you. We also provide you with a detailed description of the complications which may occur after the surgery during the consultation as it's a surgical procedure so there may be some complications depending on the way your body reacts.
Kayakriti in news



Frequently Asked Questions
If you have flat or small breast and you want to improve your breast and hip contour ratio then you are a good candidate for it. The answer will be best provided after the first consultation with Dr Amit Agarwal.
Acute pain will be there for almost a week which gradually reduces and there will be soreness and swelling which may take up to 3 weeks to subside.
You can join your work and daily routines after a week of the procedure and can start exercising after 3 weeks of it.
Yes, you have to wear it round the clock unless we suggest you to remove it.
This surgery does not affect the ducts or the areas of the breast involved in milk production. Thus, it does not affect the breast feeding.
This surgery does not affect the ducts or the areas of the breast involved in milk production. Thus, it does not affect the breast feeding.










Kayakriti Plastic Surgery & Dental Center
D-43, Near Punjab National Bank, Rajajipuram, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226017, India
Phone No. +919695940009, +919695940006
Map Location



























Social Media Presence