Complications of Arteriovenous Fistula
Dialysis is a procedure that is required in patients with kidney failure for purification of toxins from blood which was originally the function of kidneys.
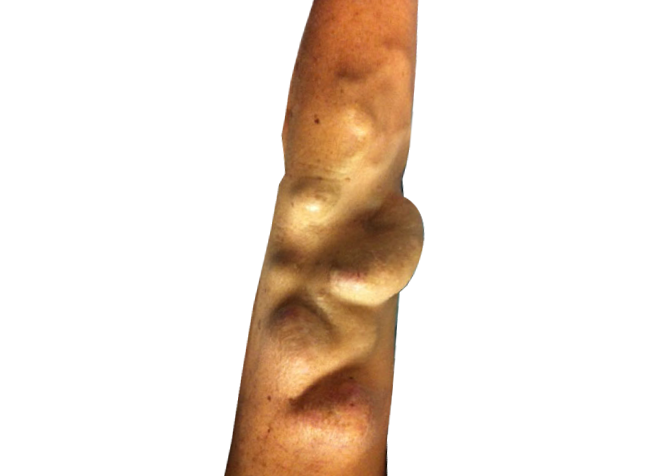
Dialysis is a procedure that is required in patients with kidney failure for purification of toxins from blood which was originally the function of kidneys. The longest-lasting and best type of dialysis access is by an arteriovenous fistula, or AV fistula which is created after surgery in left upper limb preferably. In this, a vein and an artery are joined together to facilitate the drawing of blood by the machine and its transfer back into the body during dialysis. The surgery is usually done under local or regional anaesthesia.
Arteriovenous fistulae also lead to few complications like-
- Failure of AV fistula-
Success of the surgery for AV fistula largely depends on the condition of the artery and the recipient veins in the arms and forearms region. Usually, the patients who come for AV fistula surgery have had multiple pricks in the veins of the forearm because of the need for iv access for antibiotics and blood transfusion. In such cases, walls of the veins are damaged and the quality of AV Fistula formed is not viable sometimes due to which another attempt of surgery might be required in future for fistula formation at some other site.
- Infection-
Infections like cellulitis can develop around the fistula, which manifests as localized redness and swelling and is usually easily treated with antibiotics. But serious infections are associated with aneurysmal dilation of blood vessels, blood collection or abscesses, which requires surgical incision and drainage. In few cases of active infection, however fistula needs to be ligated to prevent torrential bleed.
Localized infections occurring after puncture of AV Fistula during dialysis are treated with appropriate antibiotics if signs of inflammation are present. AV Fistula infections are very rare and all respond well to antibiotic treatment which lasts for 4-6 weeks. Ligation of the AV Fistula is required only when it becomes a source of infective embolism to the lungs.
- Aneurysm-
An aneurysm is a pathological enlargement of the blood vessel wall resulting from repetitive puncture. False aneurysms or pseudoaneurysm are hematomas located outside the vessel wall, formed due to a leaking hole in the artery, most often due to iatrogenic trauma - primarily repeated needle punctures.
Colour Doppler ultrasound can differentiate false-aneurysm expansion from a hematoma, true dilated aneurysms (blood vessel), the presence of a thrombotic mass, which enables a decision to be made on possible surgical correction.
Surgical intervention is recommended in pseudoaneurysms and aneurysms when there is a risk of perforation and ulceration, if there are episodes of bleeding or if the overlying skin is not healthy. This has to be treated surgically by excision of the mass, closure of fistula or leaking artery and making a new fistula if required usually in the same setting.
- Rupture-
Repeated punctures of fistula for dialysis or infection leads to thinning of its walls which make it weaker and rupture of fistula may follow. If ruptured, the emergency surgical management is required to control the blood loss and either ligate the fistula or repair it and make a new AV Fistula at the same time.
This is done by microvascular surgery done under microscope. After repair, extra care is taken to confirm patency of fistula and to maintain the blood flow. Blood thinning drugs are given for this.
- Stenosis-
Significant stenosis of the vessel lumen is defined as a reduction by more than 50%. Clinical suspicion of stenosis is confirmed by the presence of several factors: reduced quality of dialysis, problems with puncture, such as prolonged bleeding after AVF puncture, pain in the area of the fistula or increased venous pressure.
Thrombosis is a crucial cause of loss of function of an AVF. It usually occurs near a blockage in the area of anastomosis or vein of the fistula.
High urea in blood increases levels of homocysteine or endogenous inhibitors of NO synthase, which could be directly toxic to the inner lining of the blood vessels. Vein wall distensibility is controlled by collagen, elastin and smooth muscle. There is accumulation of collagen fibers in place of smooth muscle cells in preaccess cephalic veins, causing a decrease in the elasticity of the vein wall. This process reduces the distensibility of the veins, and thus interferes with the proper maturation of the AVF. Stenosis may also be due to compression by an abscess or hematoma.
Stenosis is diagnosed by measuring the peak systolic velocity in Doppler ultrasound. Values greater than 400 cm/s indicate the presence of stenosis; a monthly decline in flow by 20-25% is also considered significant for this type of complication. Angiography is a reliable technique for determining stenosis but is more expensive and technically demanding. Treatment involves balloon dilatation of the stenosis, stent implantation or surgical revision. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) in the treatment of AV Fistula stenosis improves fistula function and prolongs fistula survival in patients with shorter lesions ( <1 cm ), but restenosis remains the major problem.
- Congestive heart failure-
Heart failure in patients with AVFs occurs only in individuals with previously chronic heart disease. Preliminary data show a trend towards left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) in patients with an AVF. Heart failure is a medical emergency and is treated in intensive care setting. Medications to strengthen the pumping action of heart are given and to decrease the burden of work of blood pumping over the heart muscles is tried to reduce by giving medical treatment.
AV fistula-Induced Ischemia (Steal Syndrome)
In most cases, an AV Fistula does not compromise perfusion of the hand but can lead to reduced blood flow distal to the arteriovenous anastomosis, which leads to decreases oxygenation, ischemia and necrosis in diabetics and elderly people. Clinical signs include reduced movement of the wrist with a sense of coldness in the hand and a color change to pale yellow, or purple, pain at rest and during exercise and peripheral necrosis. There is evidence that the steal syndrome in risk groups may occur in 75-90% of patients after creation of an AVF. This phenomenon remains clinically asymptomatic until the moment when compensatory mechanisms for perfusion by peripheral arteries are exhausted.
Treatment of this condition is difficult and the risk of amputation of fingers and the forearm is great. Therefore, attention must be focused on prevention, which includes adequate preoperative assessment, use of Doppler ultrasound, and a precise surgical technique that involves arteriotomy no greater than 7 mm as well as being within the range of a 90-180° angle of anastomosis. Failure to use these precise surgical techniques may lead to increased resistance and reduced blood flow.
Ischemic Polyneuropathy
Ischemic neuropathy is most common in diabetic patients, especially when the brachial artery is used for creation of vascular access. It is manifested by weak forearms, in the immediate preoperative period (typically within hours), severe pain, and altered sensations. Neurological examination shows weakness in distal muscle groups and decreased sensations in the area of median nerve. The frequency of such complications varies between 1 and 10%.
- Lymphedema-
This is a condition in which there is swelling of the whole limb below the AV fistula caused by blockage of lymph draining vessels from the limb. Treatment is usually conservative in mild case where compression bandages, limb raising and rest are advised.
Know your surgeon better

Best plastic surgeon, Dr. Amit Agarwal is an American Board Certified, extensively trained, and best Plastic & Aesthetic surgeon in Lucknow. He is the Chief Plastic Surgeon heading the Department of Plastic, Microvascular, and Craniofacial surgery at Vivekananda Polyclinic and Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, U.P, India. He maintains a busy practice at Avadh and Nishat Hospital and his own center - Kayakriti Plastic Surgery & Dental Center. He was formerly a Consultant in the Department of Plastic Surgery and Burns at the prestigious SGPGI, Lucknow.
MS, DNB (General Surgery) MCh, DNB (Plastic Surgery),
MNAMS, FACS, FICS, FRCS (Edinburgh, UK)
His Credentials
Three pillars of kayakriti
Privacy
We believe your experience with us should be comfortable and hassle-free to make it one of your best lifetime experiences for yours. We, here at the clinic, take full precautions to maintain your privacy in any manner. We also provide a staff who will receive you from the gate and take you to the chamber directly if you demand.
Trust
Our Surgeon is highly qualified and internationally certified with a team of skilled staff to perform any surgical or non-surgical treatment on your body.
Safety
When you plan to undergo any surgery you should always keep in mind that it's your body and it's a surgery. We, here always keep your safety a priority and will never recommend you to undergo any such procedure which is not safe for you. We also provide you with a detailed description of the complications which may occur after the surgery during the consultation as it's a surgical procedure so there may be some complications depending on the way your body reacts.
Kayakriti in news



Frequently Asked Questions
If you have flat or small breast and you want to improve your breast and hip contour ratio then you are a good candidate for it. The answer will be best provided after the first consultation with Dr Amit Agarwal.
Acute pain will be there for almost a week which gradually reduces and there will be soreness and swelling which may take up to 3 weeks to subside.
You can join your work and daily routines after a week of the procedure and can start exercising after 3 weeks of it.
Yes, you have to wear it round the clock unless we suggest you to remove it.
This surgery does not affect the ducts or the areas of the breast involved in milk production. Thus, it does not affect the breast feeding.
This surgery does not affect the ducts or the areas of the breast involved in milk production. Thus, it does not affect the breast feeding.










Kayakriti Plastic Surgery & Dental Center
D-43, Near Punjab National Bank, Rajajipuram, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226017, India
Phone No. +919695940009, +919695940006
Map Location



























Social Media Presence